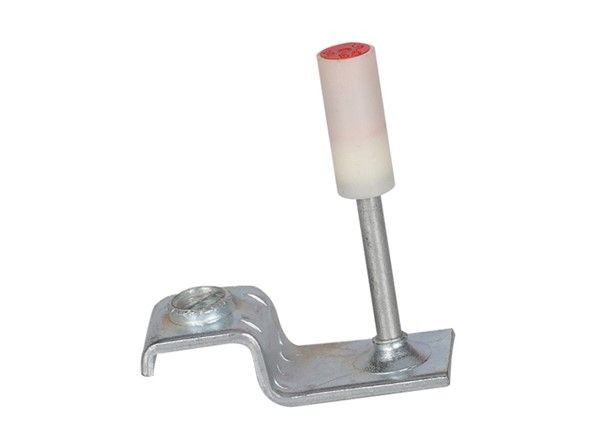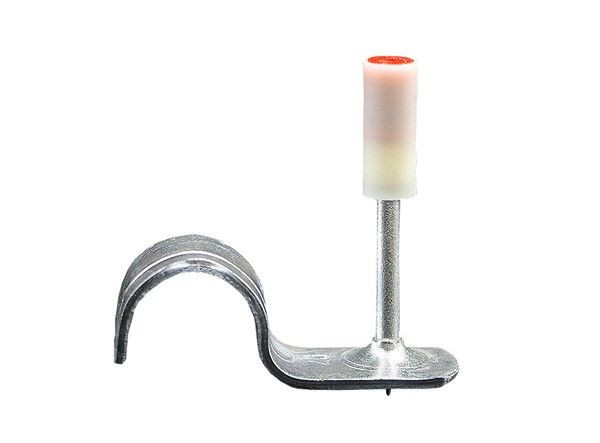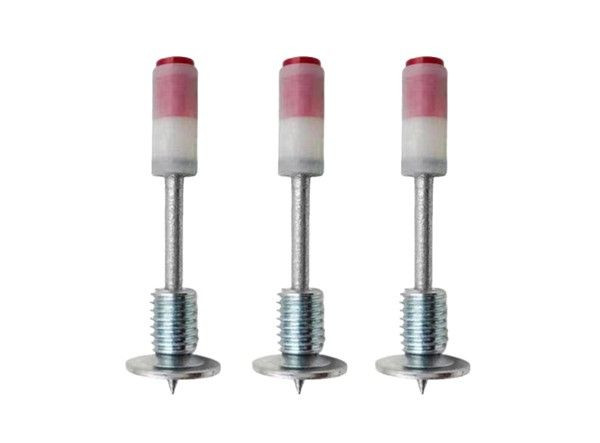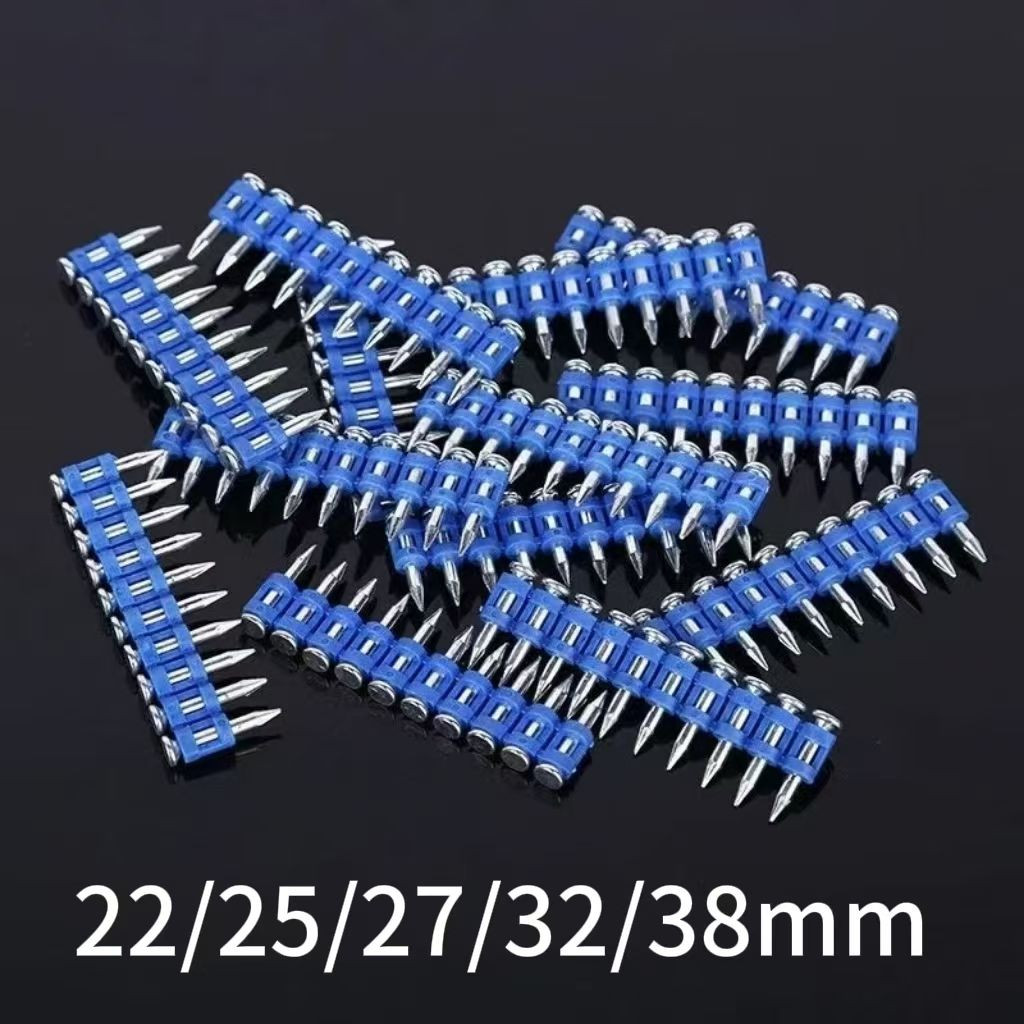

Products
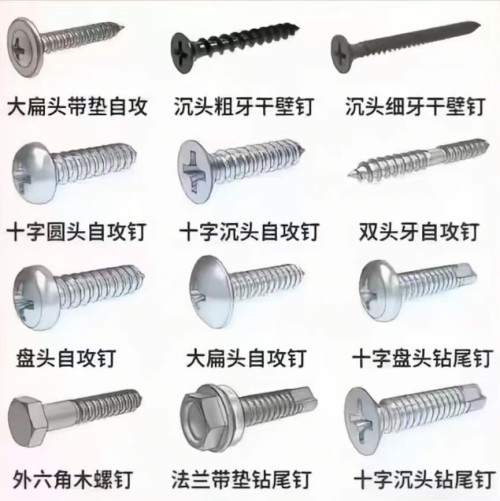
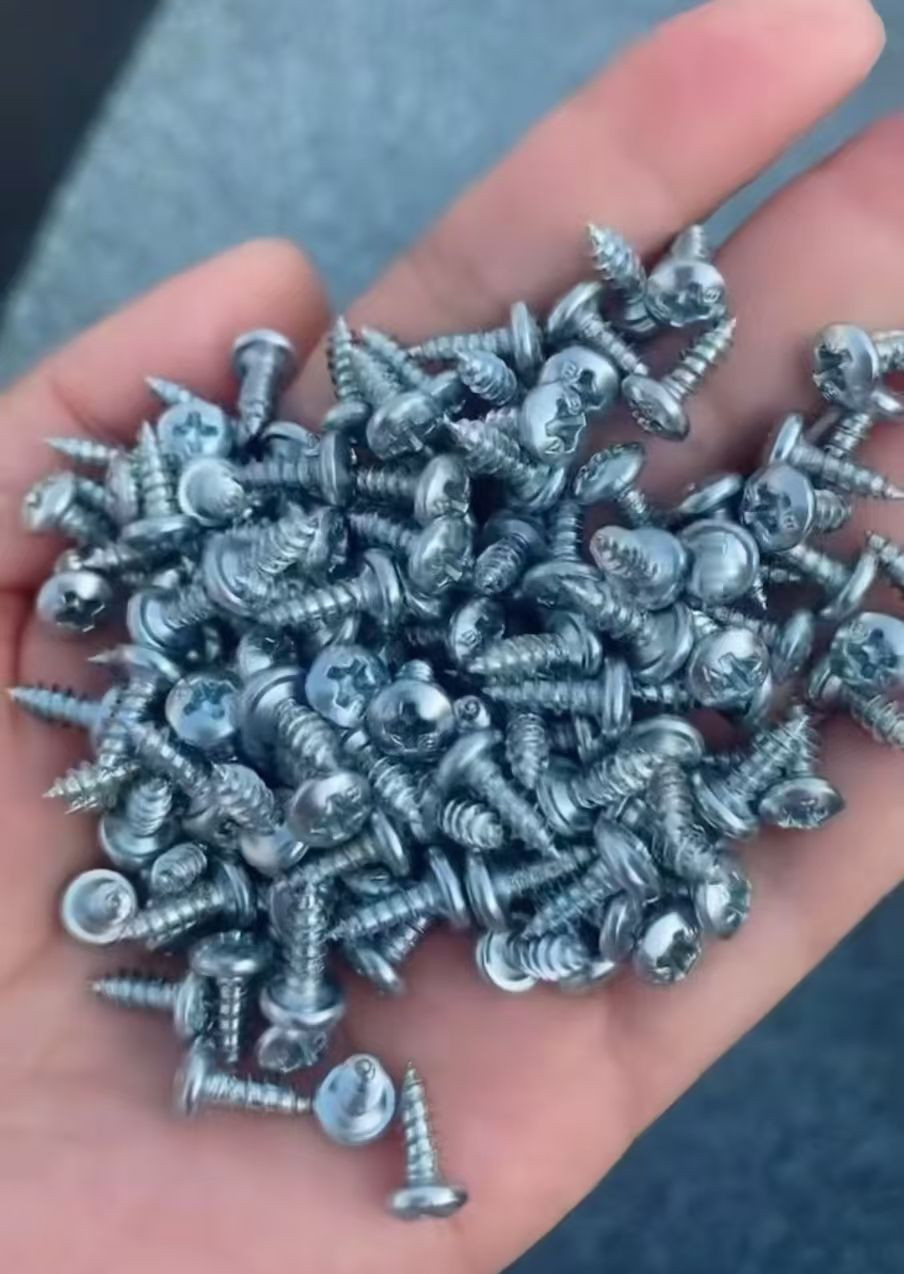

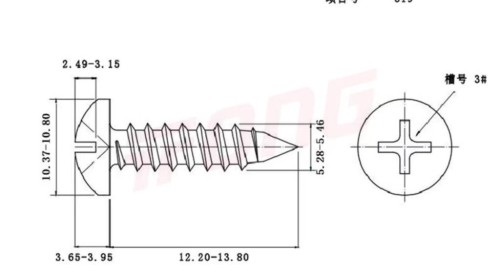


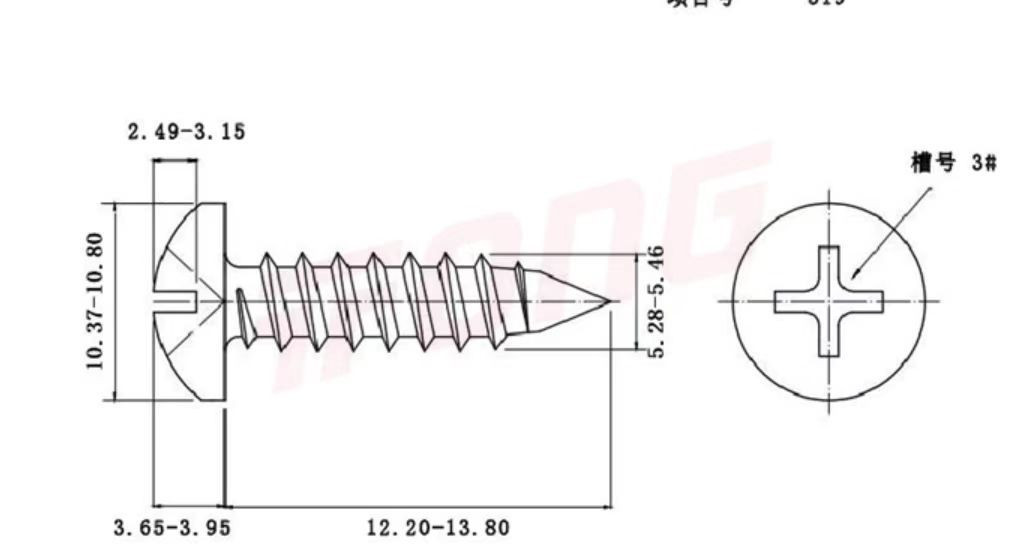

Description:
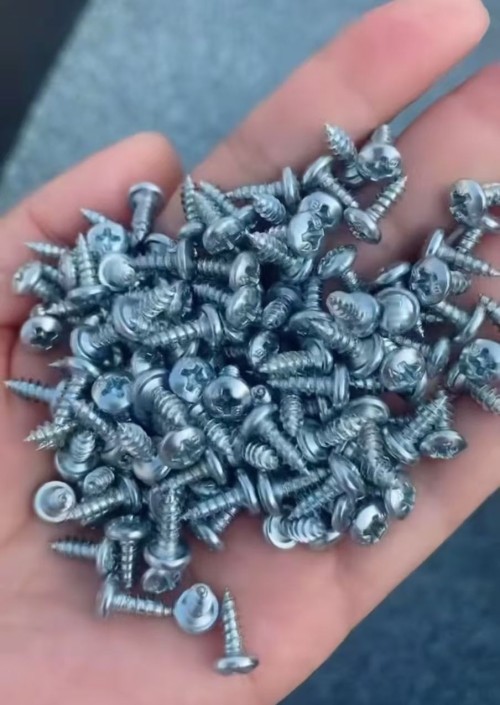
Thread Specification Thread specification indicates the size of the screw thread, and metric and imperial units are commonly used. In the metric system, examples include M2, M3, M4, etc. The number represents the major diameter of the thread (in millimeters). For instance, M3 means the major diameter of the thread is 3 millimeters. In the imperial system, inches are used as the unit, such as #4, #6, #8, etc. The larger the number, the larger the thread size. Different thread specifications determine the compatibility between the screw and the threaded hole of the connected part. Fine - thread screws are suitable for applications with high anti - loosening requirements, while coarse - thread screws are commonly used for general fastening. Nominal Length The nominal length refers to the length of the screw shank (excluding the head), with units of millimeters or inches. Common metric specifications are 6mm, 8mm, 10mm, 12mm, etc.; imperial specifications include 1/4 inch, 3/8 inch, 1/2 inch, etc. When selecting, the thickness of the connected part needs to be considered. Generally, it is necessary to ensure that there is sufficient thread engagement length after the screw is screwed in. Usually, there should be an additional 2 - 3 thread pitches after penetrating the connected part. Head Type Common head types of pan - head self - tapping screws include pan head (Pan Head), countersunk head (Countersunk Head), oval head (Oval Head), etc. The pan head has a rounded top, providing a large bearing area, which is convenient for tightening with tools. It is suitable for applications that require large torque and head support area. The countersunk head allows the screw head to be flush with the surface of the connected part, which is aesthetically pleasing and non - protruding. It is commonly used in places where high surface flatness is required. The oval head combines the characteristics of the pan head and the countersunk head. The head has a certain curvature, combining aesthetics and good torque transmission performance. Slot Type The slot type is the shape of the groove on the screw head for matching with a screwdriver. Common types include slotted (Slot), Phillips (Phillips), Torx (Torx), etc. The slotted screw is operated with a flat - blade screwdriver. It is simple but prone to slipping when tightening. The Phillips screw is used with a Phillips screwdriver, which has good centering performance and is not easy to slip, and is widely used. The Torx screw matches with a Torx screwdriver, with high torque transmission efficiency and good anti - loosening performance. It is commonly used in products with high fastening requirements. Surface Treatment Although not a core part of the specification model, surface treatment is often mentioned in the specification description. Common surface treatments include galvanizing (Zn), nickel - plating (Ni), blackening treatment, etc. Galvanizing can improve the anti - rust ability of the screw, and there are various types such as colorful galvanizing and white galvanizing. Nickel - plating not only prevents rust but also makes the screw surface more beautiful and smooth. The blackening treatment has a low cost and can also provide a certain anti - rust effect.




